Healthcare organizations continue to be prime targets for malicious actors. OCR data in a recent Health IT Security article showed more than 127 breaches reported so far in 2022 had impacted over 6 million individuals. In addition to increased threats, the healthcare industry has the highest cost per incident at $9.23 million, up $2 million more from 2020.
Healthcare organizations are racing to implement best practices and meet ever-changing compliance requirements. Industry and government organizations like CHIME, AEHIS, HIMSS, CISA, HHS and the FBI are all trying to provide help.
There’s also a bevy of cybersecurity frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK, HITRUST, NIST CSF, and regulations such as HIPAA to provide guidance.
Unfortunately, the path forward isn’t always clear, and the many approaches available to decision-makers can be more of a hindrance than an advantage at times.
Technology and delivering healthcare have never been more entwined. In fact, a recent Ponemon study noted a link between ransomware and an increased mortality rate. However, healthcare leaders may find it daunting if every IT decision seems critical; after all healthcare is about the patients, and everything else is secondary.
Enter the 405(d) Task and Program, a collaborative effort between industry and the federal government to ingest all the many cybersecurity paths for healthcare organizations to help provide a guided map.
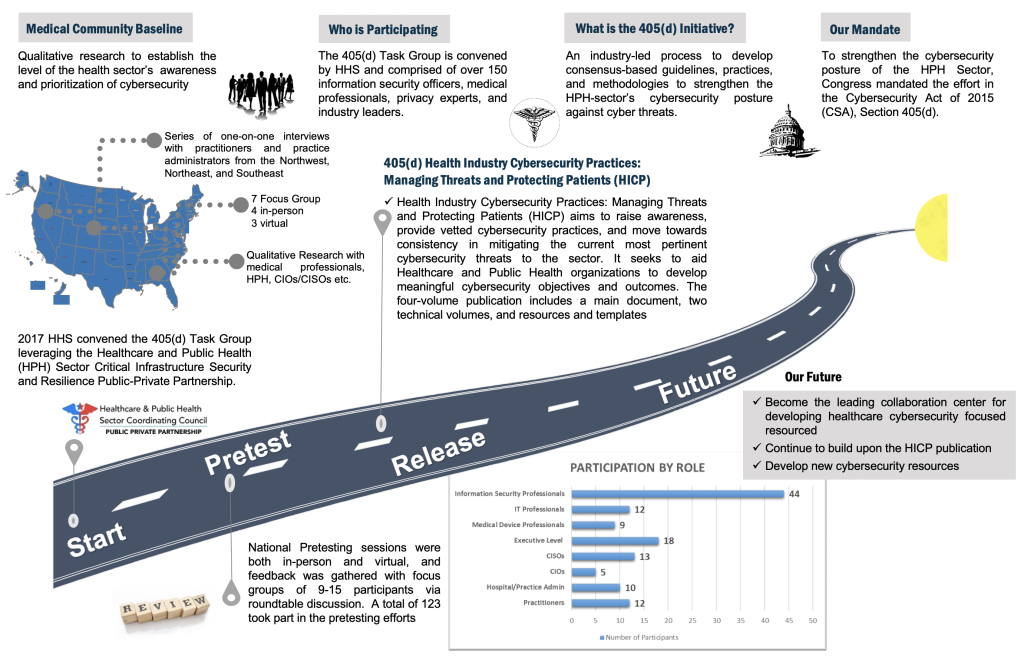
As part of the program, the 405(d) Task Group developed Health Industry Cybersecurity Practice (HICP): Managing Threat and Protecting Patients.
HICP is not a compliance checklist or framework. It’s a “how to” resource incorporating threat landscape intel and offering best practices that align with recognized frameworks like NIST CSF. The latest version of the 405(d) framework explores five current threats and presents ten practices to mitigate those threats.
405(d) resources also include the HICP Threat Mitigation Matrix, a tool to help you map your journey and give you actionable practices to accomplish them.
In addition, you can visit the 405(d) website to access further resources and learn more.

