Alert essentials:
A threat actor can execute arbitrary code in FortiManager using an API vulnerability currently exploited in the wild.
Version upgrades are available for FortiManager 7.2.8 and 7.4.5. More fixes are expected to be released in the coming days.
Detailed threat description:
A critical function in Fortinet’s FortiManager “fgfmd” daemon is missing authentication.
If an unauthenticated bad actor obtains a certificate from any Fortinet device owned or compromised, the missing authentication can be used to execute arbitrary code remotely.
Attacks are reported in the wild, and this flaw, with a 9.8 CVSS score, has already been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities list. Fortunately, there are no current indications that malware or backdoors are being installed via the method. However, exfiltration of files containing configurations and credentials has been observed.
Customers known to have vulnerable FortiManager versions privately received mitigation instructions from Fortinet about ten (10) days ago. Since then, the bypass has been fixed in two available version upgrades. Additional version upgrades with fixes are expected to be released soon. Until then, perform the following mitigations on vulnerable devices.
Mitigations:
- Utilize the set fgfm-deny-unknown enable command to prevent devices with unknown serial numbers from registering to the FortiManager.
- Create a custom certificate when creating the SSL tunnel and authenticating FortiGate devices with FortiManager.
- Create an allowed list of IP addresses for FortiGate devices that are allowed to connect
*Instructions on performing mitigations can be found in Fortinet’s advisory.
Impacts on healthcare organizations:
Whenever healthcare systems are attacked, care delivery is delayed, inevitably putting patient safety at risk.
Affected products / versions:
FortiManager versions impacted are:
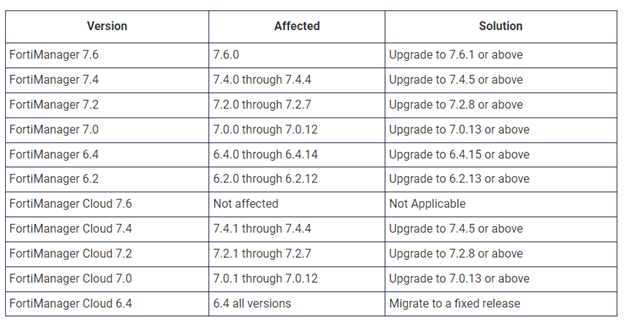
*FortiManager Cloud 7.6 is not affected
CVEs
CVE-2024-47575
IOCs
Log entries
type=event,subtype=dvm,pri=information,desc=”Device,manager,generic,information,log”,user=”device,…”,msg=”Unregistered device localhost add succeeded” device=”localhost” adom=”FortiManager” session_id=0 operation=”Add device” performed_on=”localhost” changes=”Unregistered device localhost add succeeded”
type=event,subtype=dvm,pri=notice,desc=”Device,Manager,dvm,log,at,notice,level”,user=”System”,userfrom=””,msg=”” adom=”root” session_id=0 operation=”Modify device” performed_on=”localhost” changes=”Edited device settings (SN FMG-VMTM23017412)”
IP addresses
45.32.41.202
104.238.141.143
158.247.199.37
45.32.63.2
Serial Number
Rogue devices are using the serial number FMG-VMTM23017412
Creation of Files
/tmp/.tm
/var/tmp/.tm
*Note that file IoCs may not appear in all cases.
Recommendations
Engineering recommendations:
- Upgrade vulnerable versions as soon as a fix is available
- Perform mitigations for protection on vulnerable versions that do not have a fix currently
Leadership/ Program recommendations:
- Look for private notifications from Fortinet regarding the use of vulnerable Fortinet solutions
- If your organization has a vulnerable FortiManager and a notice was not received, reach out to your Fortinet contact to be included in future notices
Fortified recommends applying patches and updates where possible and only after adequate testing in a development environment to ensure stability and compliance with organizational change management policies.
References:
- Fortinet PSIRT: PSIRT | FortiGuard Labs
- CISA KEV: CISA Adds One Known Exploited Vulnerability to Catalog | CISA
- FortiManager configuration: https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiManager/Technical-Tip-FortiManager-data-configuration-and/ta-p/351748


